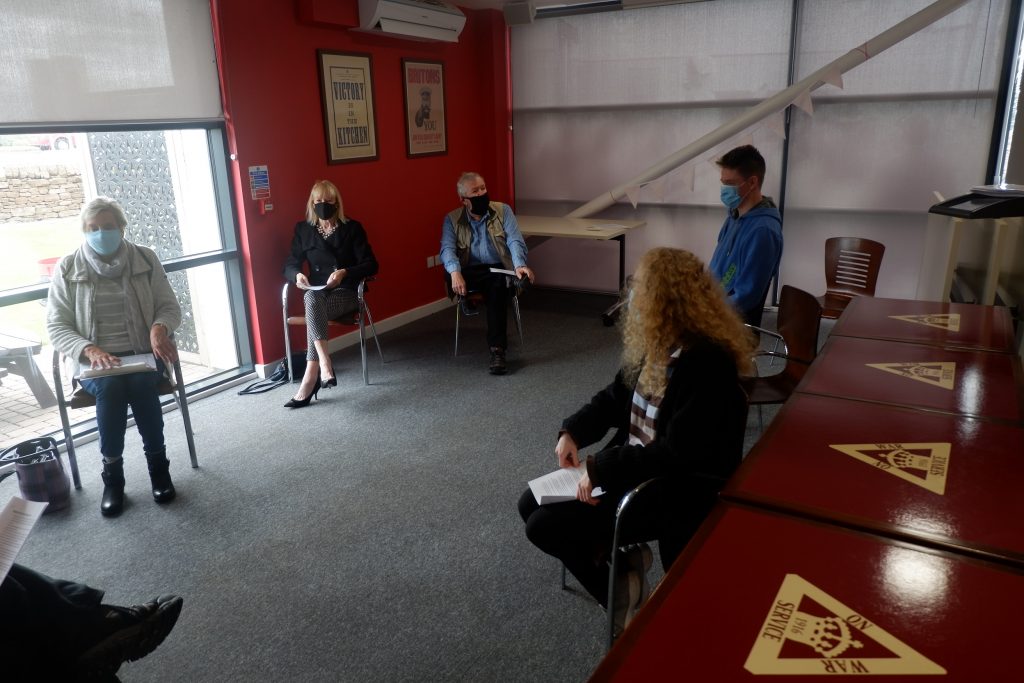
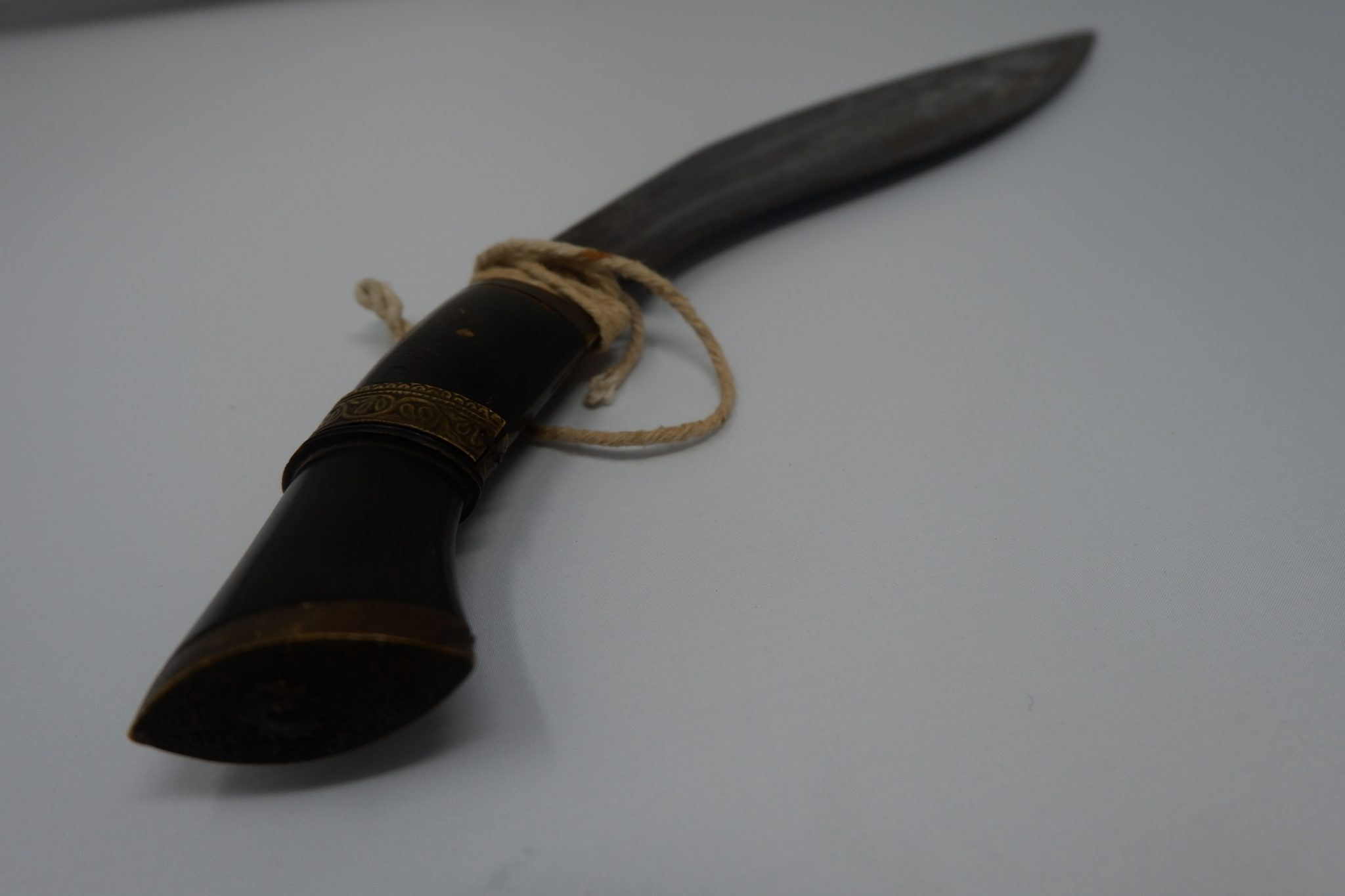
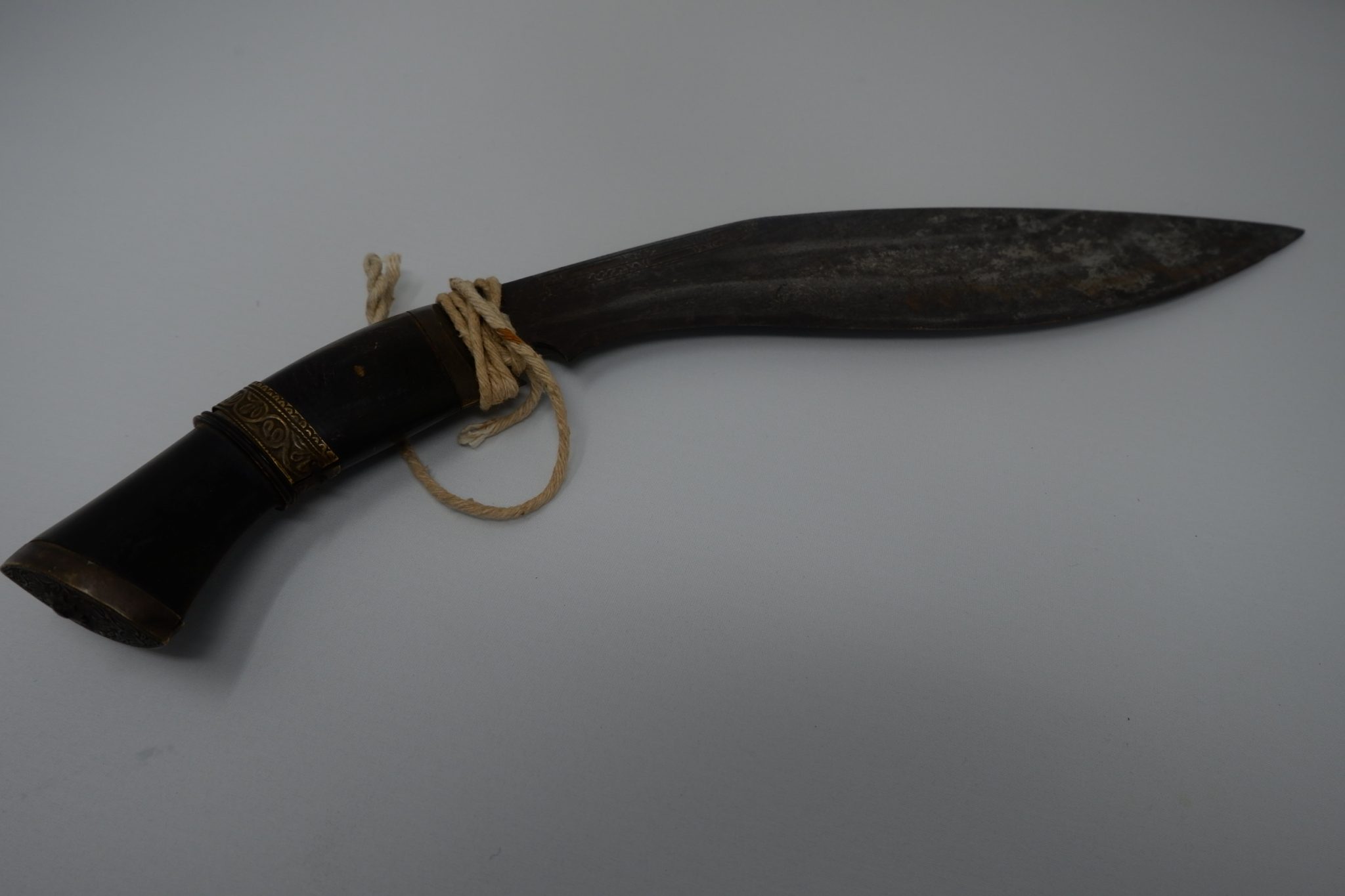
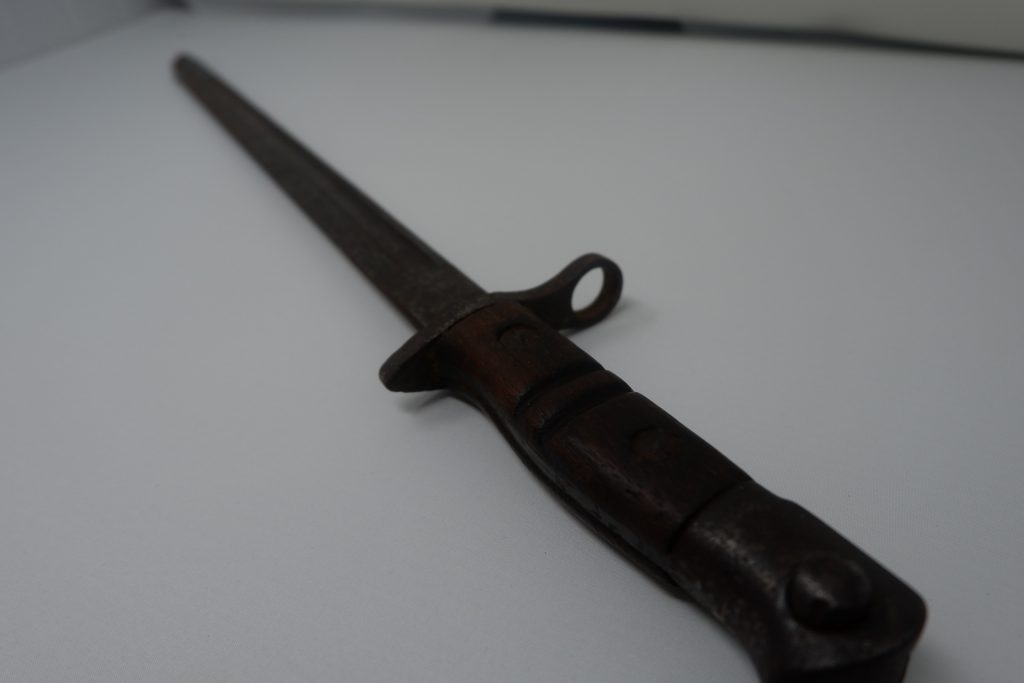
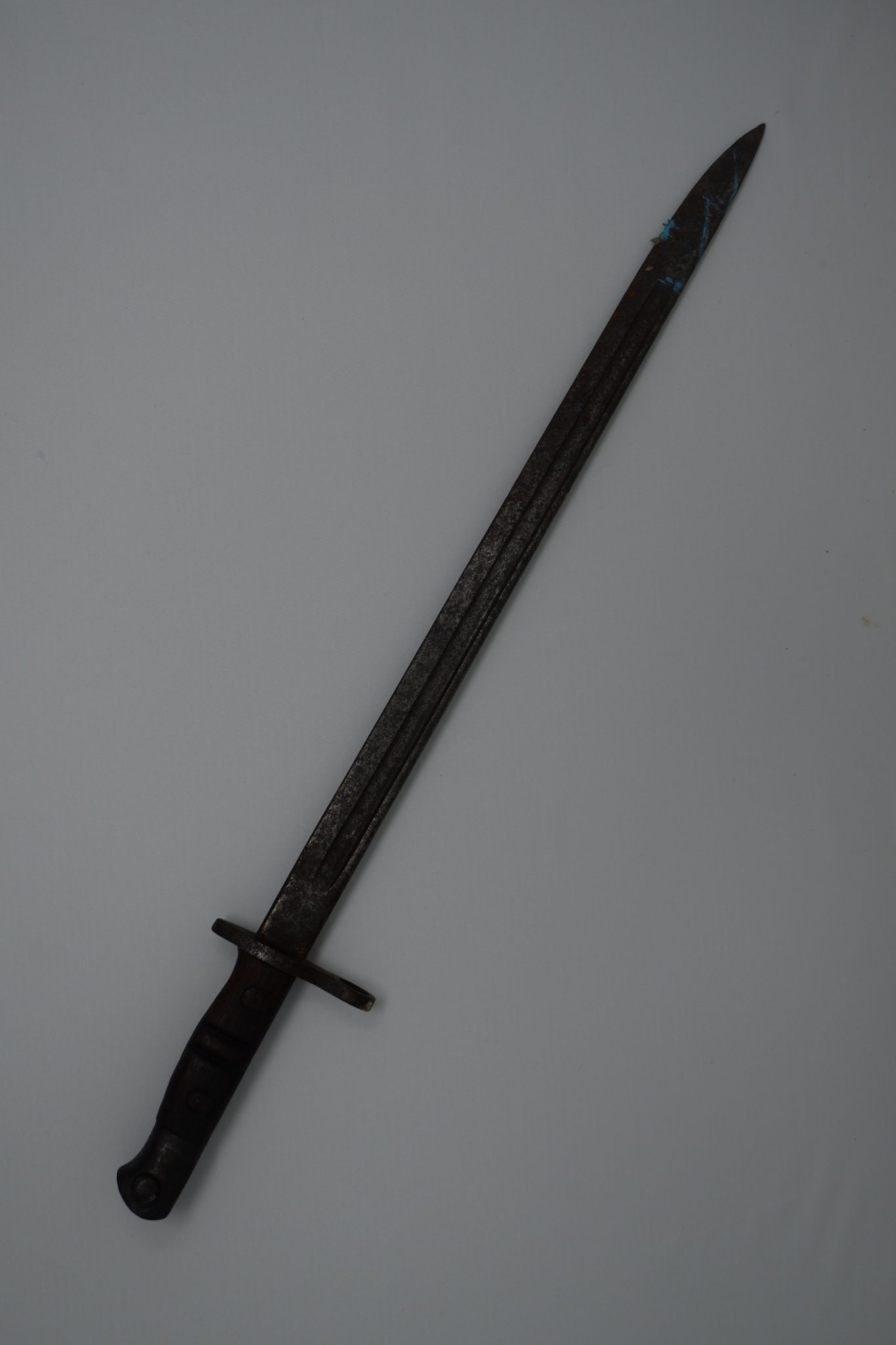
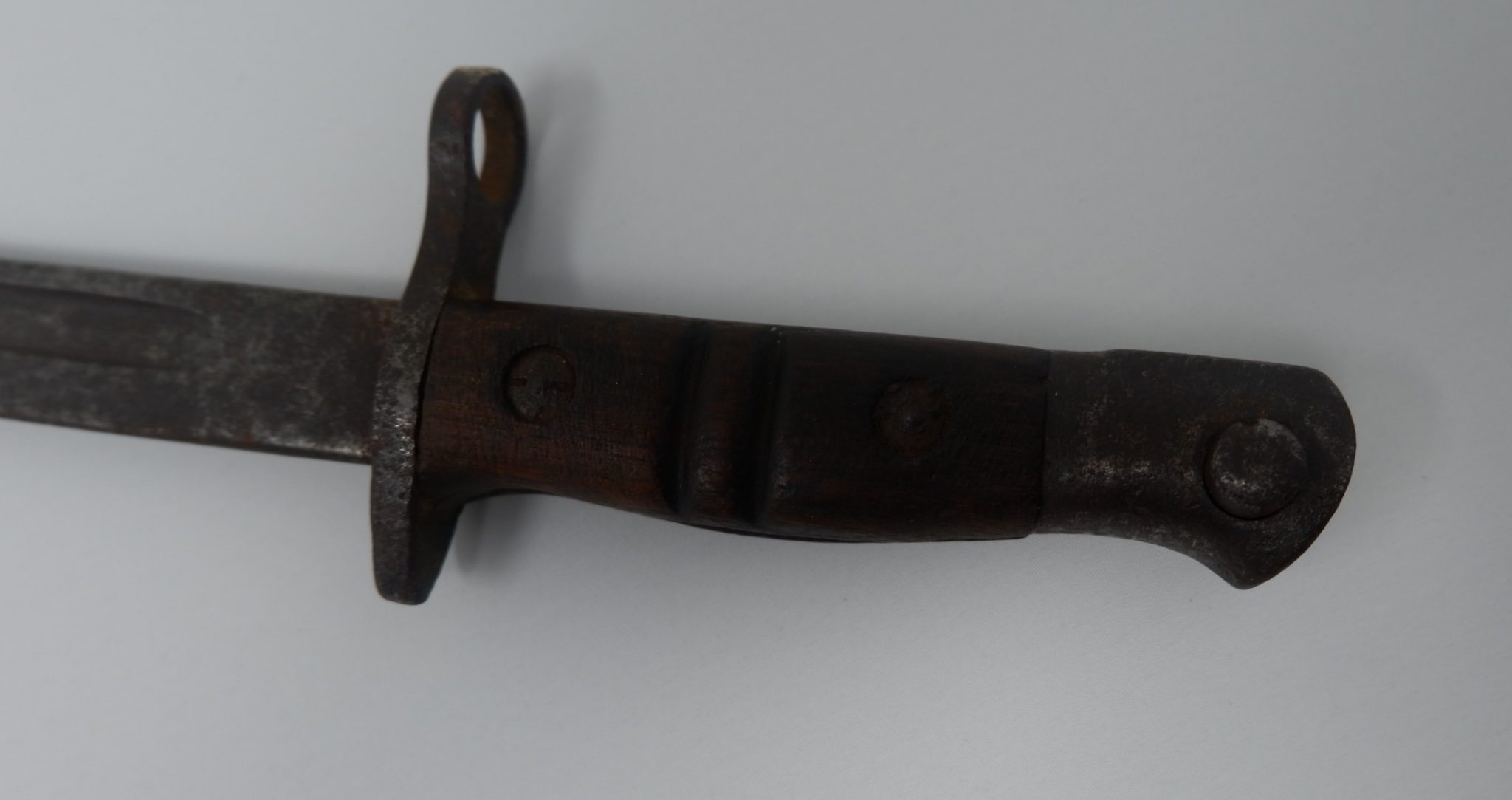
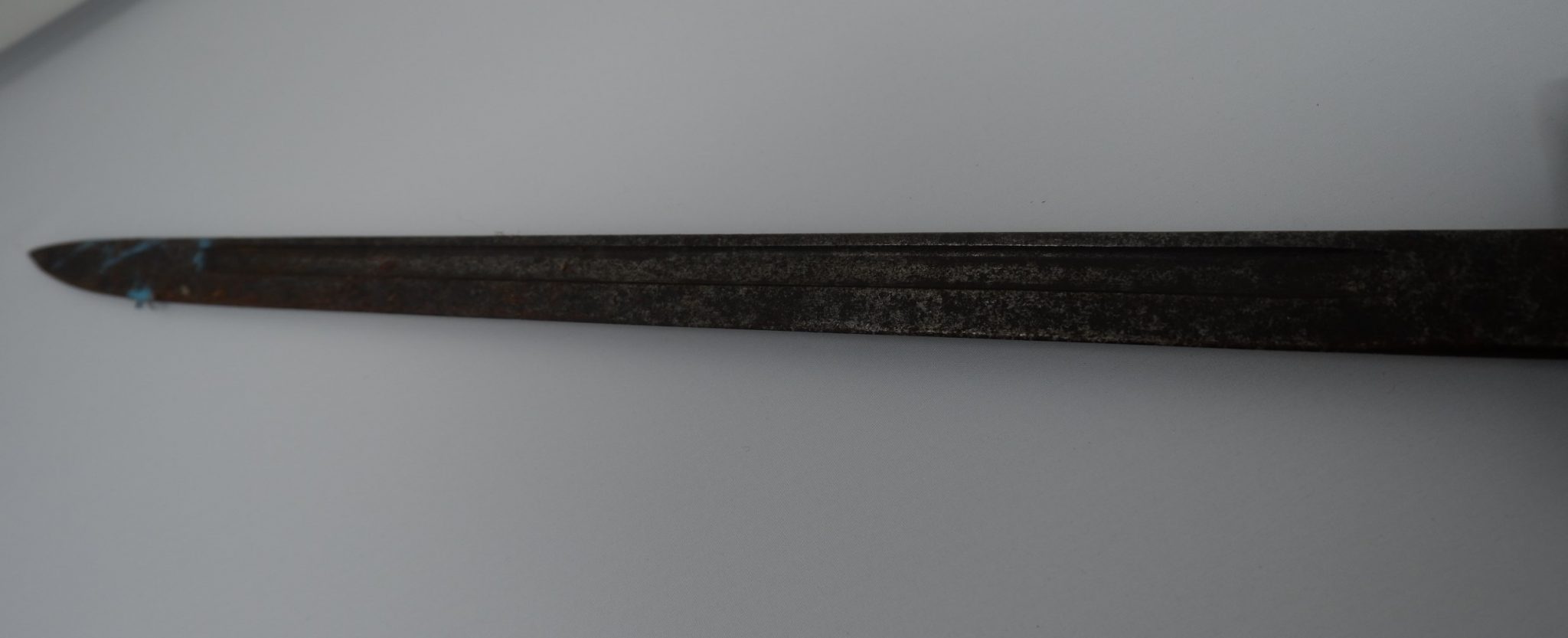
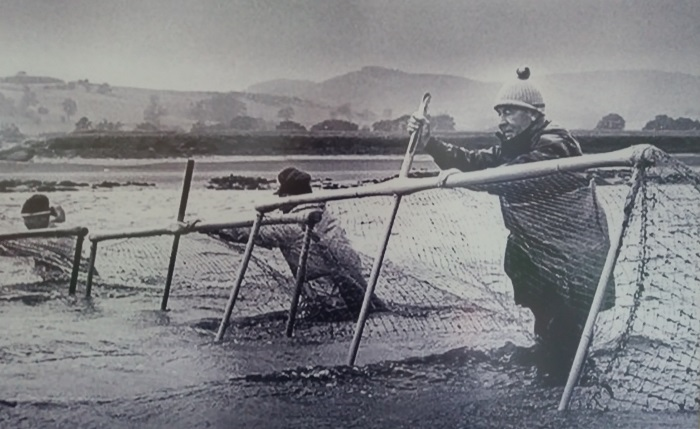
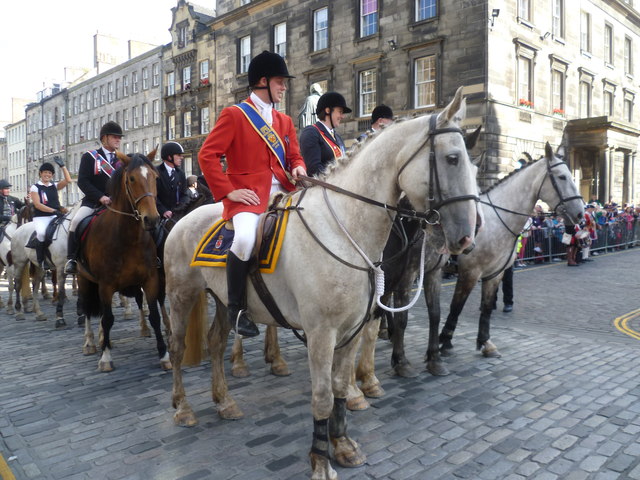
We are now taking email bookings from Tuesday 4th August , when we re-open , until Sunday 9th August. Make sure you get a time slot by booking with us before you come. We will allow only one family group in every ten minutes to ensure your safety. All you need to do is email info@devilsporridge.org.uk with the approximate time you want to arrive, give your name, size of group and phone contact details . We will get back to you with an exact slot time when you are guaranteed priority entry.