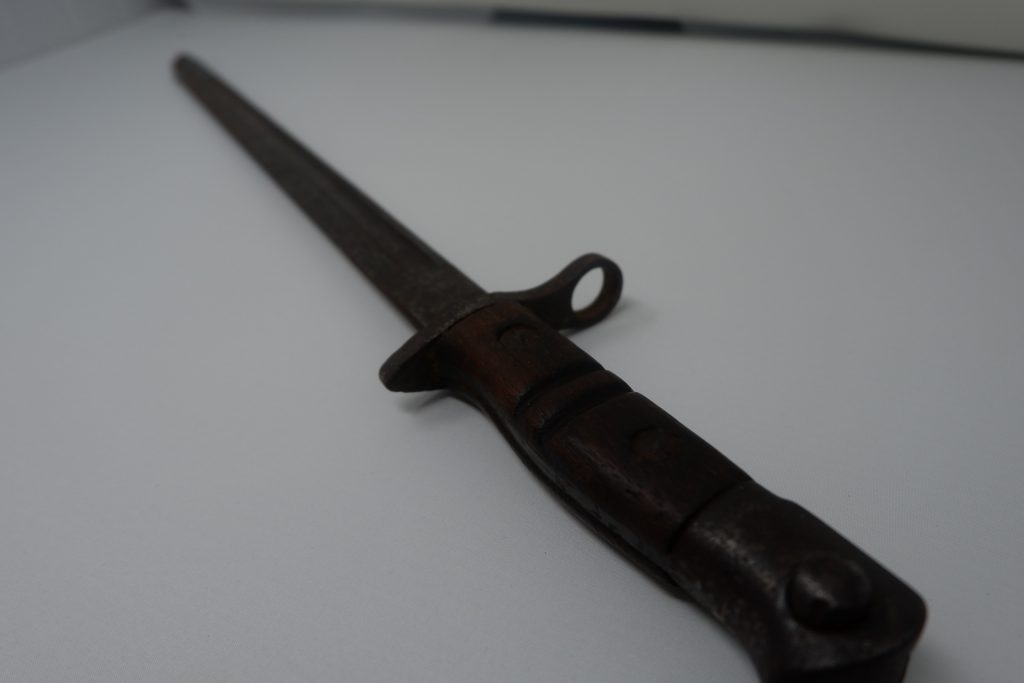
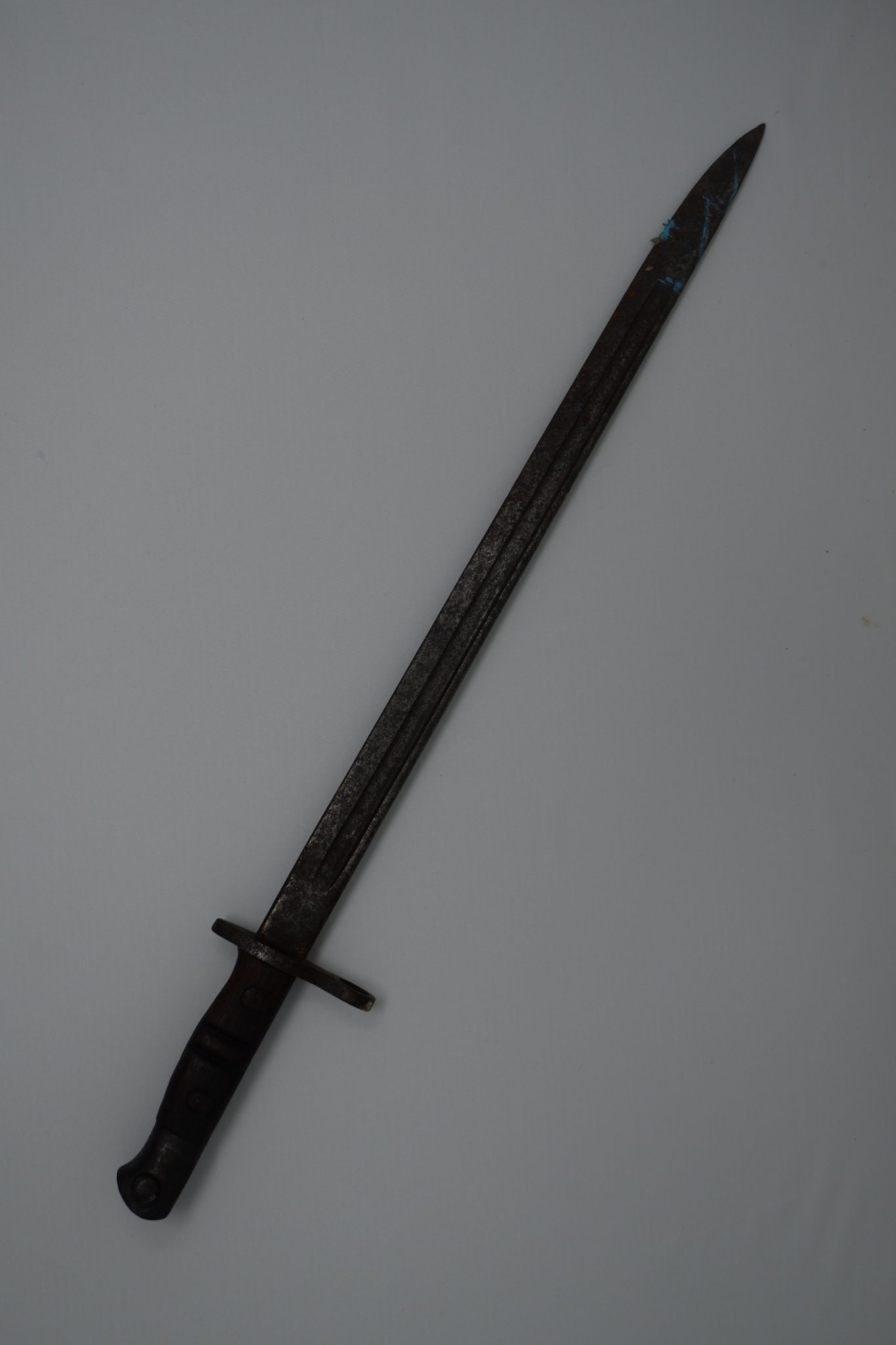
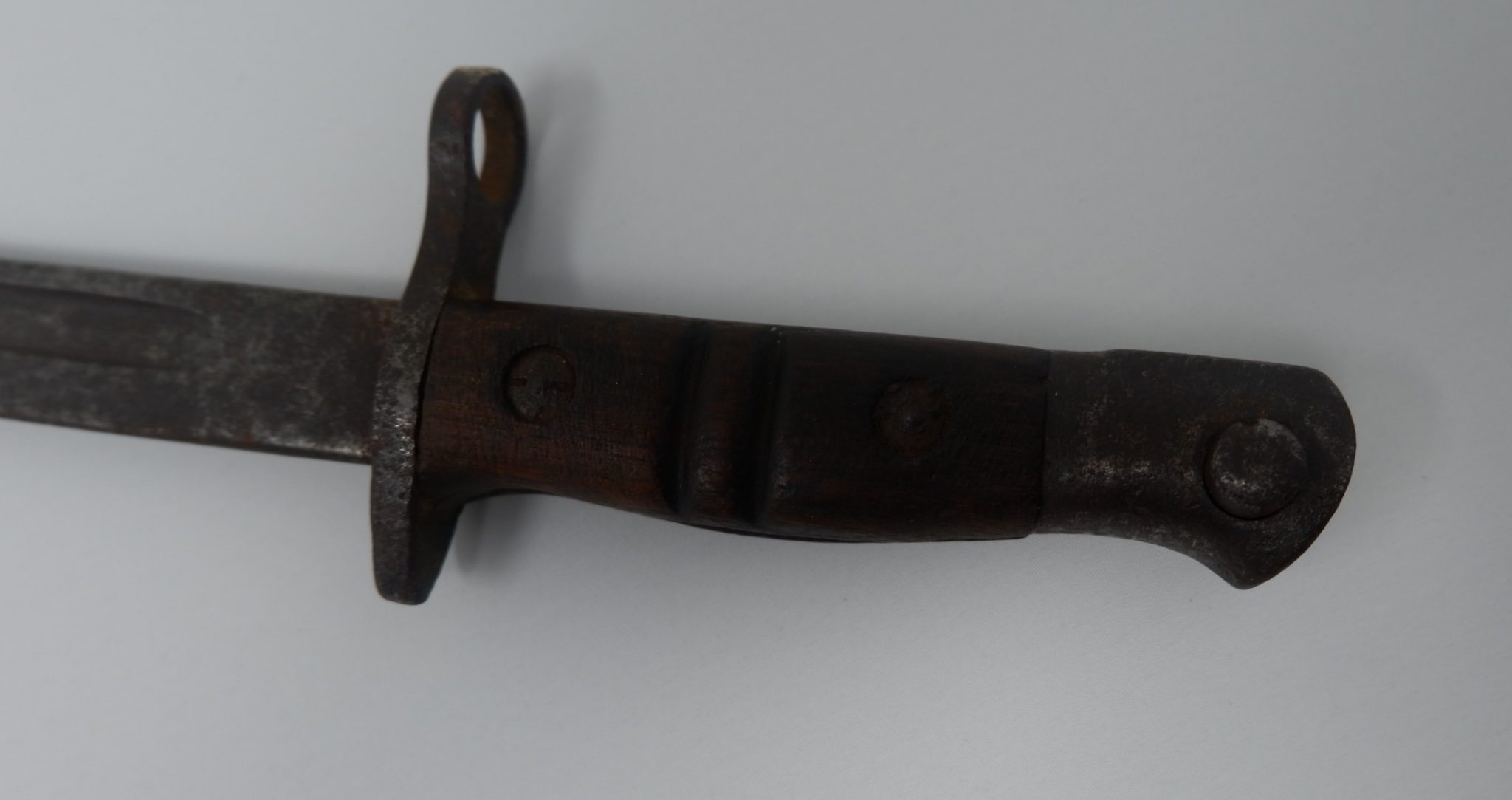
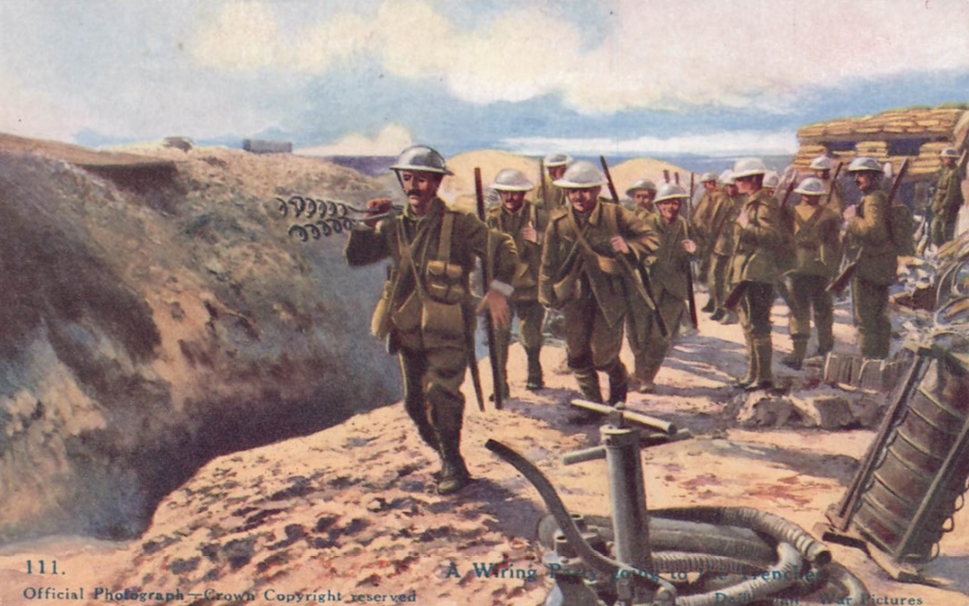
This First World War bayonet was recently brought into the Museum by one of our volunteers and is an American M1917 bayonet which was used in World War One, World War Two, Korean War and in the Vietnam War.
It was first used by American soldiers in WW1 on the Western Front. A sword bayonet design, the M1917 bayonet design was based on the British pattern 1913 bayonet. While designed specifically for the M1917 rifle, the bayonet was fitted for use on all the ‘trench’ shotguns at the time. The US continued to use the WW1-made M1917 bayonets during World War Two because of large stockpiles left over. The new trench guns being procured and issued were still designed to use the old M1917 bayonet.
The bayonet was then called upon again during the Korean war for issue due to the various trench guns still being in use. In 1966 procurement orders were let for brand new production M1917 bayonets. Stockpiles had finally run out, and new Winchester 1200 trench shotguns were being issued. These were issued in limited quantities during the Vietnam War. It was not until towards the end of the Vietnam War that new military shotguns were designed to use the newer knife bayonets.