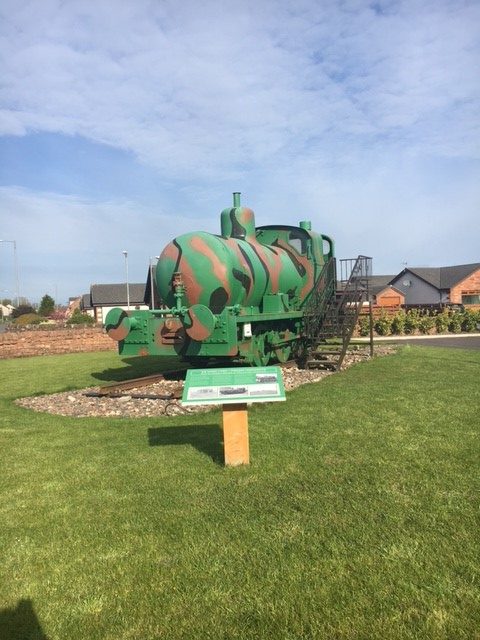
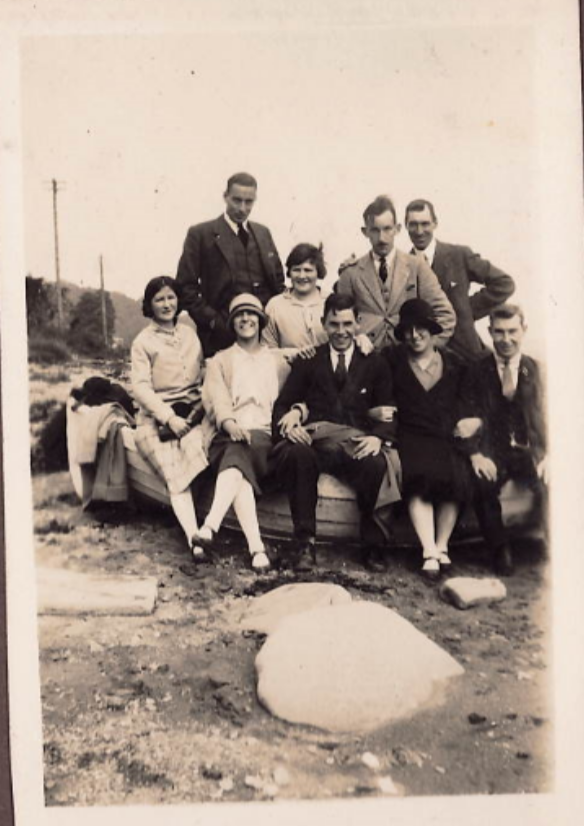
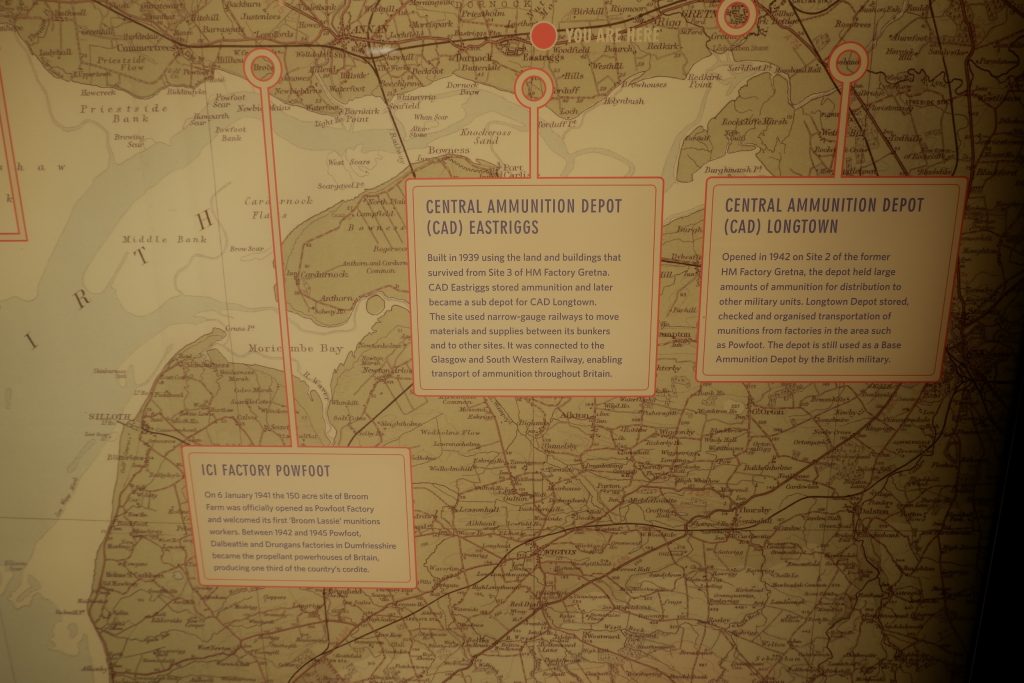
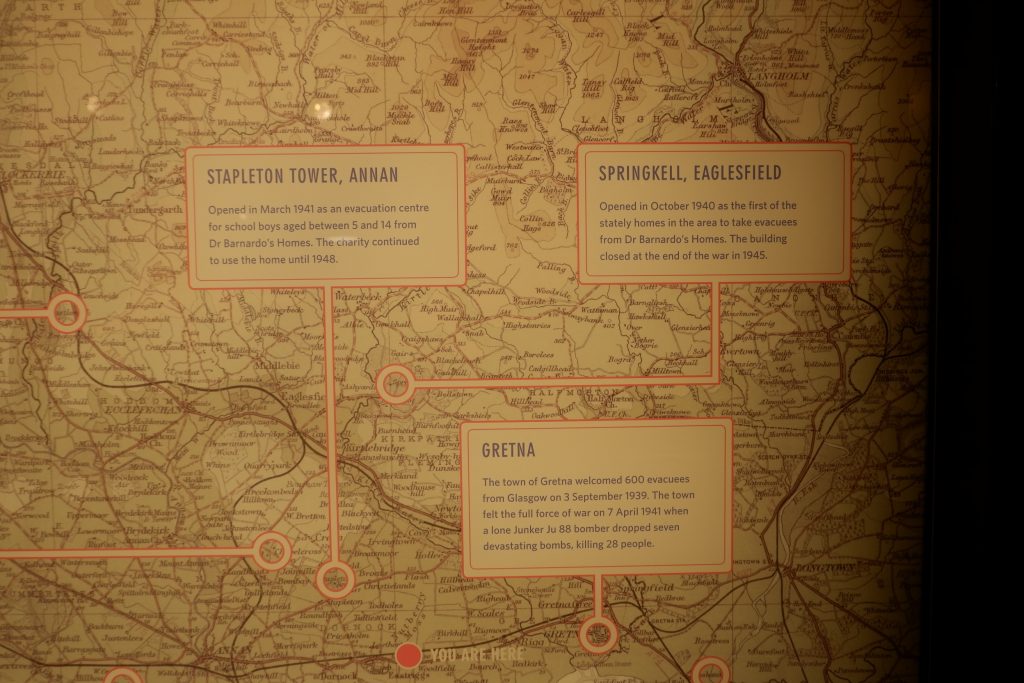
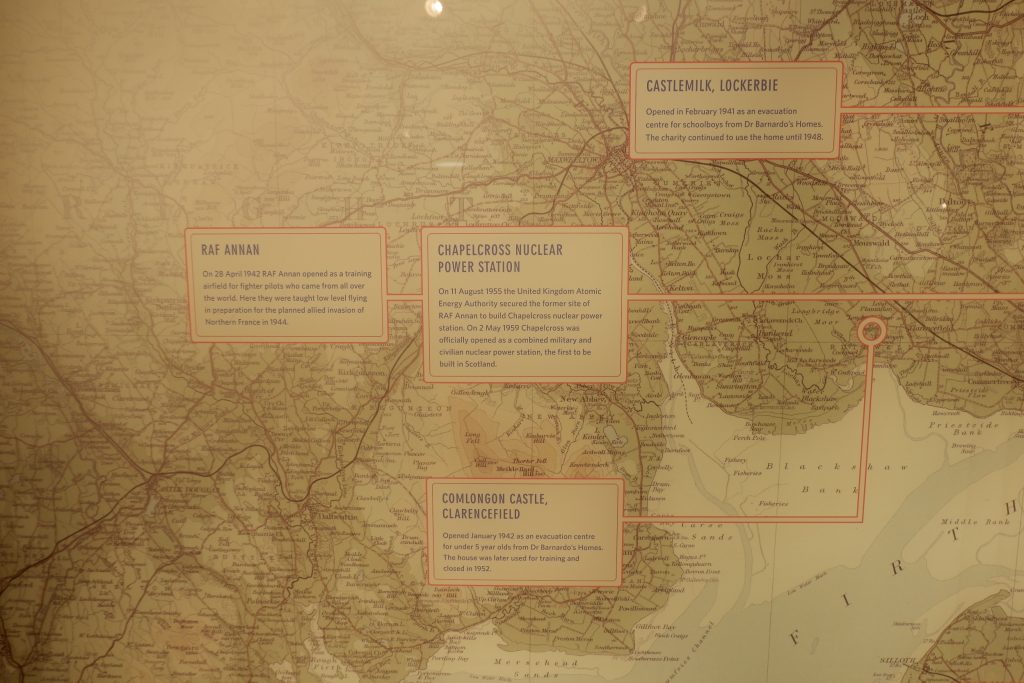
Outside The Devil’s Porridge Museum there stands a train, a fireless locomotive called Sir James, which was built and used in World War One. By the time it came to the Museum, it was in a rusty and poor state of repair. The Museum spent a lot of time and money restoring the engine and it is now one of our most popular displays.

This engine was used to transport the ‘devil’s porridge’ paste through HM Factory Gretna (the greatest munitions factory on earth at that time, it stretched nine miles from Dornock in Scotland to Longtown in England). The paste was made into cordite, a propellant in the English side of the Factory. Cordite went inside all the bullets and shells used in World War One.

Sir James is an unusual locomotive. It is powered by steam but there is no fire inside. This was a safety precaution as the Factory produced explosive material and the train was used to transport it. There was a genuine concern that there might be a major explosion (there were several fires and explosions here during World War One but the safety record was remarkably good given that 30,000 people worked at the Factory in total and we know of only twelve deaths directly attributable to accidents).

Sir James was built by Andrew Barclay of Kilmarnock, Scotland and in World War One, it would have been charged up with steam from an external boiler before setting off. For these locomotives to work, it was necessary to have three charging stations en route to maintain pressure. These ‘crazy green and brown patchwork’ camouflaged fireless locomotives could pull ten loaded wagons and return the empty wagons on one charge of steam.

At the end of the War, the Factory eventually closed and much of the machinery was sold off. Sir James was sold in 1924 to the Metropolitan Electric Power Supply Company at Brimsdown Generating Station and then in 1975 to the Lakeland and Haverthwaite railway before joining us at the Museum and being restored to its former glory in 2011.

If you enjoyed this article you might be interested in the following items from our online shop…
HM Factory Gretna’s Unique Railway System Booklet
Sir James Postcard